Table of Contents
5 C’s of Cyber Security an Introduction
In the digital era, where data breaches and cyber-attacks are increasingly common, robust cyber security measures have become paramount for organizations of all sizes. The 5 C’s of cyber security—Change Management, Configuration Control, Credentials Management, Continuous Monitoring, and Cyber security Education—serve as foundational pillars in constructing a secure digital environment. These principles guide the implementation of effective security strategies, ensuring the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of information technology systems.
1.Change Management
In-depth Overview:
Change management is the disciplined approach to proposing, evaluating, implementing, and reviewing changes within an organization’s IT environment. It’s vital to ensure that changes do not introduce new vulnerabilities and that they align with the organization’s security policies and compliance requirements.
Advanced Strategies for Implementation:
- Change Proposal Evaluation: Implement a structured process for evaluating the security implications of proposed changes.
- Automated Deployment Tools: Use automated tools to standardize and streamline the implementation of changes, reducing human error.
- Post-implementation Review: Conduct thorough reviews after implementing changes to ensure they have not adversely affected the security posture.
2 Configuration Control
In-depth Overview:
Configuration control involves maintaining the security and operational integrity of software and hardware through the management of their configurations. It prevents unauthorized modifications that could compromise security and ensures that systems are always configured according to the latest security standards.
Read Also:
Cyber Security Basics for Beginners: Understanding the Foundations for a Safer Digital World
Microsoft: Breach of Company Source Code by Russian Hackers
Advanced Strategies for Implementation:
- Configuration Baselines: Establish and maintain secure configuration baselines for all systems and continuously update these as security standards evolve.
- Automated Configuration Management Tools: Utilize tools to automate the enforcement of configuration policies and the detection of deviations.
- Decommissioning and Disposal: Ensure secure decommissioning and disposal processes for hardware and software, preventing data leaks.
3 Credentials Management
In-depth Overview:
Credential management is critical for controlling access to systems and data. It encompasses the creation, storage, use, and deletion of credentials, ensuring that access is granted only to authenticated and authorized users.
Advanced Strategies for Implementation:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Beyond 2FA, implement MFA to add multiple layers of security.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): Use PAM solutions to manage and monitor accounts with elevated privileges.
- Regular Credential Audits: Perform periodic audits of credentials to identify and remove unused or obsolete accounts.
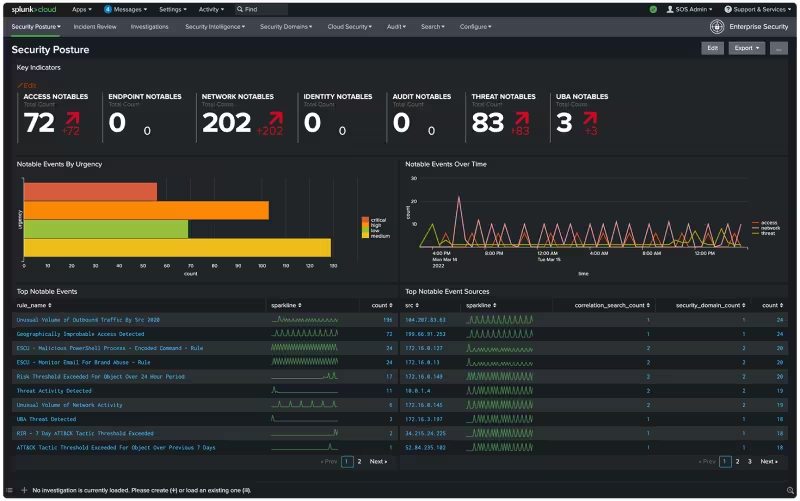
4 Continuous Monitoring
In-depth Overview:
Continuous monitoring is the ongoing process of detecting, analyzing, and responding to cyber security threats and vulnerabilities. It provides real-time visibility into the security state of IT assets.
Advanced Strategies for Implementation:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Implement SIEM systems for real-time analysis and logging of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware.
- Behavioural Analysis: Employ behavioural analysis tools to detect anomalous activities that may indicate a security incident.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Leverage threat intelligence feeds to enhance detection capabilities with information on the latest cyber threats.
5 Cyber Security Education
In-depth Overview:
Cyber security education focuses on training users to understand the importance of security practices and to recognize potential threats. An informed workforce can significantly reduce the risk of security breaches.
Advanced Strategies for Implementation:
- Customized Training Programs: Develop role-specific cyber security training that addresses the unique risks faced by different departments.
- Gamified Learning Experiences: Incorporate gamification to increase engagement and retention of cyber security concepts.
- Continuous Learning Culture: Foster a culture of continuous learning where cyber security awareness is an integral part of the organizational ethos.

FAQs:
How does change management contribute to cyber security?
Change management ensures that all changes to IT systems are assessed, tested, and documented, reducing the risk of introducing vulnerabilities and maintaining compliance with security policies.
What is the significance of configuration control in preventing cyber-attacks?
Configuration control helps prevent attacks by ensuring systems are hardened against known vulnerabilities, reducing the attack surface available to potential attackers.
How can effective credentials management prevent data breaches?
By securing the creation, storage, and use of credentials, organizations can ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive systems and information, thus preventing unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
In what ways does continuous monitoring enhance cyber security?
Continuous monitoring provides real-time insights into security threats and anomalies, enabling rapid detection and response to potential cyber security incidents.
Why is cyber security education considered a critical defence mechanism?
Educated users can recognize and avoid phishing attempts, malicious links, and unsafe online practices, acting as the first line of defence against cyber threats.
By meticulously applying the principles outlined in the detailed exploration of the 5 C’s of cyber security, organizations can significantly bolster their cyber defences, safeguarding their digital assets against the evolving threat landscape.